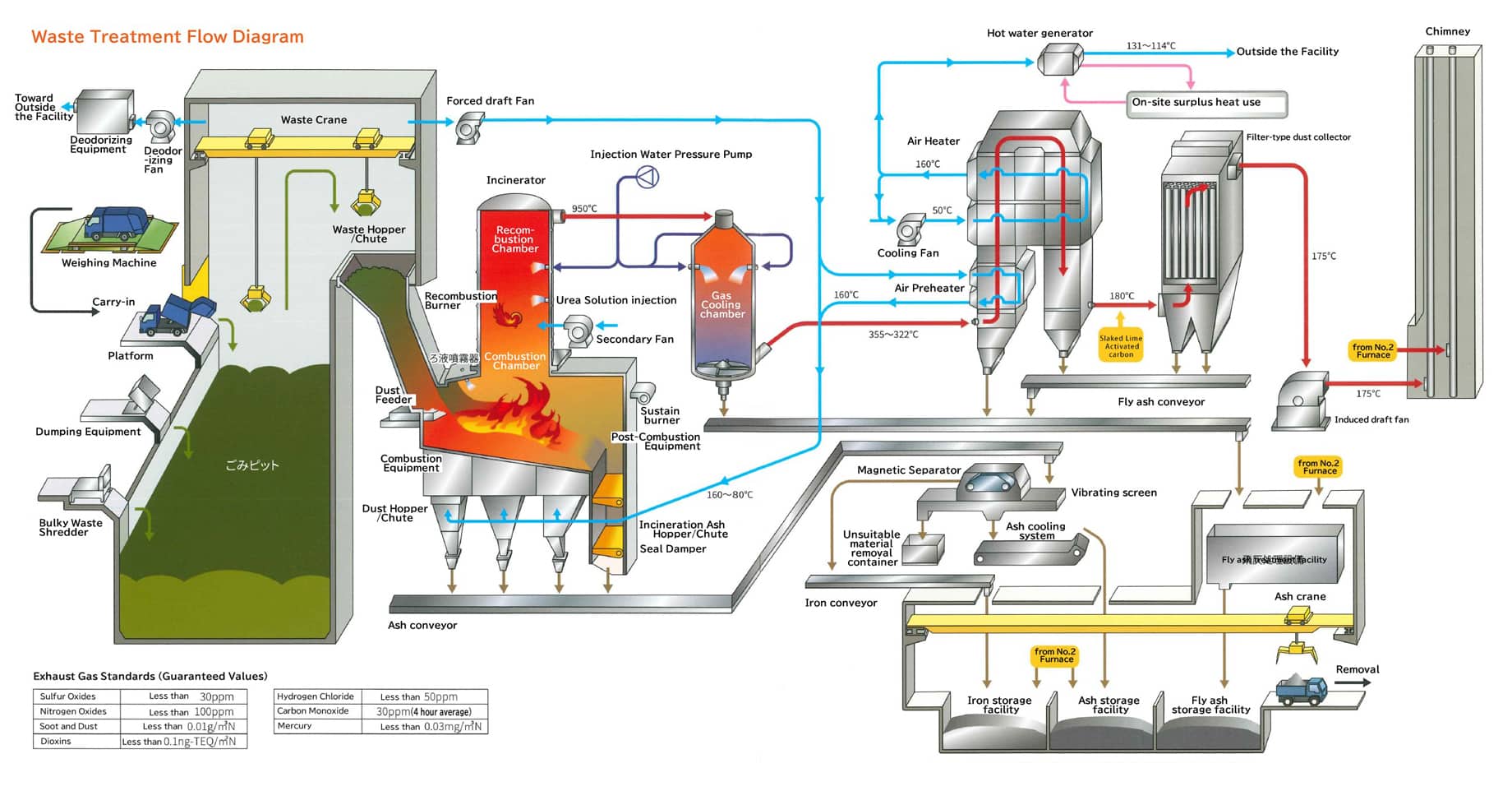
In Japan, most municipal waste generated by businesses and households, as well as industrial waste generated by business activities, is rendered harmless through incineration.
Waste is dumped from the platform into a waste pit, where it is agitated and then dumped into an incinerator by a waste crane.The dumped waste is rendered harmless through complete combustion in the incinerator.Exhaust gases containing many hazardous substances and incineration ash, generated during waste combustion, are appropriately treated in a downstream exhaust gas treatment device before being released.
Sanwa Engineering designs and manufactures filter-type dust collectors, which are central to this exhaust gas treatment, as well as heat exchangers, which recover thermal energy.
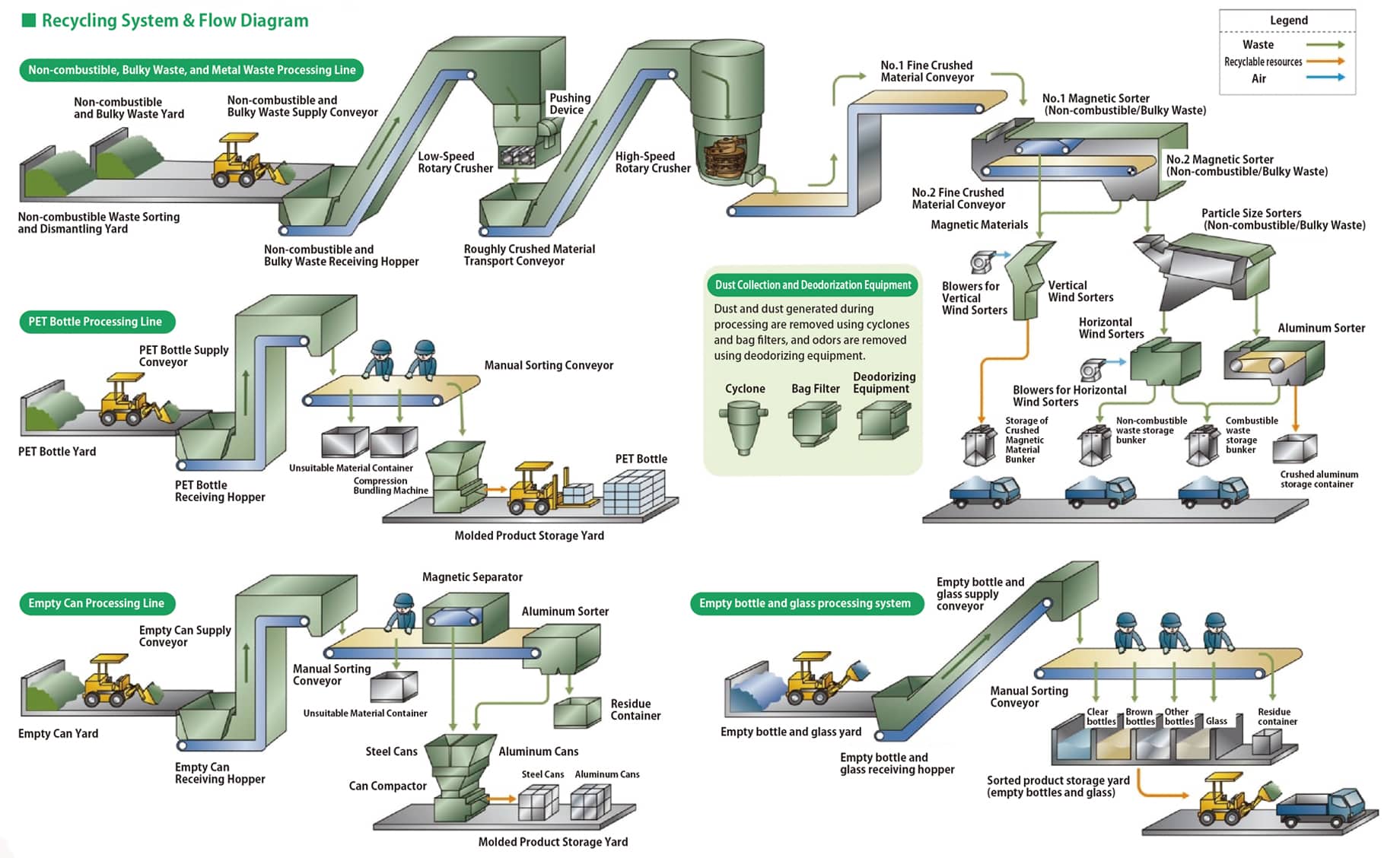
In many cases, material recycling Facilities are located adjacent to waste incineration Facilities.
Collected waste is roughly sorted by treatment system and then deposited through the receiving yard (feed port).
Oversized and non-combustible waste is crushed by a shredder and then separated into iron, aluminum, glass, and other non-combustible materials by subsequent sorting equipment.
Plastics are also sorted by type, packaged, and transported to a post-processing facility.
Sanwa Engineering handles everything from the design and manufacture of various transport equipment to delivery and trial operation, and is committed to improving efficiency and labor-saving throughout the Facility.
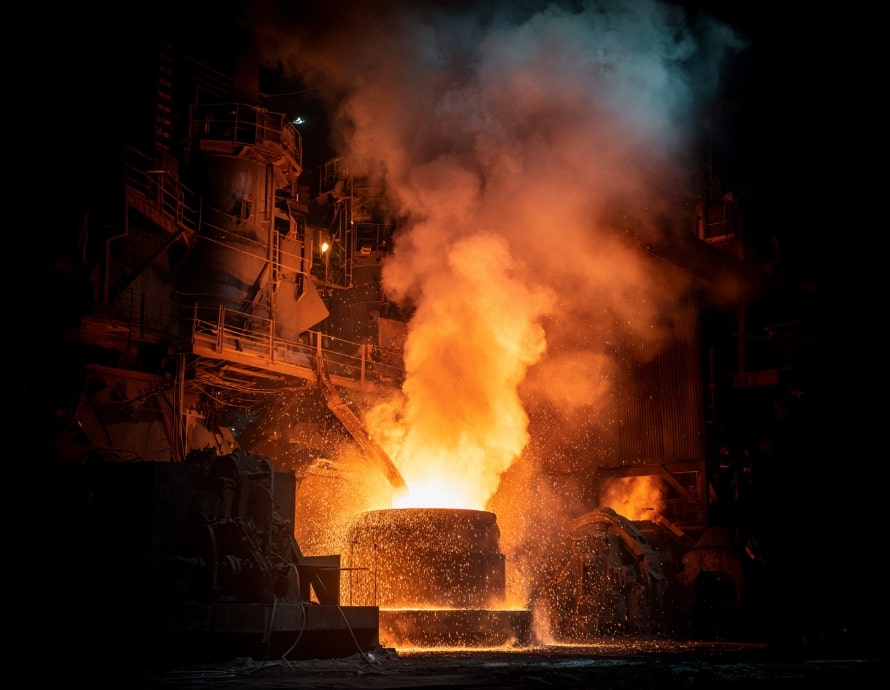

In electric arc furnace Facility, scrap iron is melted and recycled using electricity to produce steel products such as steel bars and sections.
Melting scrap iron generates large amounts of high-temperature gas, which contains dust. In addition to the equipment used to produce steel products, electric arc furnace Facility require equipment to prevent this exhaust gas from filling the factory.
Sanwa Engineering manufactures dust collection equipment that sucks in and cools the exhaust gases emitted by electric arc furnaces and captures the dust.
Electronic substrates are used in all electronic devices that enrich people's lives around the world, including AI, computers, smartphones, automotive controls, satellite communications, and navigation systems.
A radiant impregnation plant is a facility that produces a product called "prepreg," the base material for electronic substrates.
An impregnation plant involves three processes: soaking, drying, and curing.
A glass cloth (web) as thin as 10 μm thick is impregnated with a resin (varnish) diluted with an organic solvent. A radiant panel then uses far-infrared rays to heat the web from within, evaporating the solvent and half-curing the resin.
Sanwa Engineering handles all aspects of the plant, from planning and design to equipment manufacturing, delivery, and start-up.
